Why does the baby never have an arch at birth? Why do some babies’ heels look crooked? Why do some babies develop foot arches when they grow up, but some babies can’t?
Today Ideastep brought you this article to bring everyone to understand flat feet and their secondary effects, and arouse everyone’s attention to flat feet in children~
Arch formation
The formation of the arch of the foot is caused by the uneven growth rate of the plantar bones and ligaments during the growth and development of children. It should be known that the hands and feet are the fastest parts of the limb’s bone growth. The growth rate of ligaments cannot keep up with the growth of bones. With the original attachment points of bones and ligaments unchanged, as the growth of bones accelerates, the longitudinal direction is lost. The growth space has to be changed by the position of the inner cuneiform bone, navicular bone, and other joints to form an upward growth space, and gradually form the arch of the foot.
With age, children’s activities such as walking, running, and jumping increase, which promotes stronger foot muscles and more favorable ligaments, which play a strong role in fixing and supporting the arch height and shape stability.
Epidemiological investigation of flat feet
Flat feet are abnormal foot bone morphology, muscle atrophy, ligament contracture, or chronic strain caused by some reasons, causing the longitudinal arch of the foot to collapse or lose elasticity. The study found that the incidence of flat feet in infants under two years of age was 100%, and the arches began to appear gradually at the age of 3-4 until the arch development in the pre-adolescent period tended to be completed, and the incidence of flat feet in 12-year-old children was 12.03%. Sui Yuelin et al.’s 2005 study on the incidence of flat feet in adolescents aged 3-12 found that the incidence of flat feet in 12-year-old children was 32.0% for men and 22.2% for women. Studies have shown that the incidence of flat feet decreases with increasing age.

Zhang Yuefang and Sui Yuelin’s survey on the incidence of flat feet in children found that after more than 20 years, there has been a significant change in the period. The detection rate of flat feet in children of the same age (12 years old) has nearly doubled after 20 years. It is believed that in the 1970s, due to the limitations of living conditions and technological level, children were more involved in housework, and the entertainment was mainly outdoor simple running, jumping, and climbing, which can promote the fullness of the foot muscles and strengthen the firmness of the ligaments.
In addition, stress stimulation is a favorable factor to promote bone growth, and proper load is the basic condition for the normal development of bone, and it plays a vital role in the formation and maintenance of the arch of the foot.
However, since the 1990s, living conditions have improved, students’ participation in housework has decreased, and entertainment has been dominated by “static” activities such as computers and television, and the foot muscles and ligaments have not been fully exercised. In addition, the increase in obesity among adolescents and long-term wearing of tourist shoes are also reasons for the increase in the incidence of flat feet.
The difference between flat feet and flat feet
Flat feet are the normal arches of the feet during a certain period during the growth of children and have no adverse effects on the daily activities, running, jumping, and speed of the human body. There are also world champions in flatfoot athletes, such as the 110-meter hurdles world record holder Robles.
Flatfoot refers to a flat deformity that is caused by the collapse of the arch of the foot and the flat medial longitudinal arch of the foot, which results in abnormal foot anatomical structure and load-bearing line and is accompanied by symptoms such as fatigue or pain. disease.
Analysis of the stress of flat feet on children’s ankles
In children with flat feet, due to congenital or acquired factors, the height of the arch of the foot is lost, the foot loses the original cushioning mechanism, and the scaphoid bone collapses, the plantar ligament and the toe aponeurosis are elongated, the deltoid ligament is loose, and the hindfoot is short. Wait for change.

Effects on the feet
In children with flatfoot, the arch becomes shorter after the arch is lost, which relaxes the tibial anterior and posterior muscles, reduces the ability to maintain the arch and aggravates the formation of flatfoot. The peroneus brevis loses the antagonism of the tibial anterior and posterior muscles, resulting in excessive traction, hypertonicity, supination, and abduction of the forefoot and valgus of the hindfoot.
Effects on the ankle
Excessive valgus of the calcaneus in children with flatfoot causes the axis of calcaneal movement to deviate from the outside of the calcaneal tuberosity, which cannot match the articular surface of the talus at the central axis, and the subtalar joint tends to be horizontal. In addition, the medial collateral ligament is loose, the lateral ligament loses resistance, the alignment of the talar-navicular joint complex is abnormal, and even the talar navicular or subtalar joint subluxation occurs, which causes the head of the talus to shift forward and downward, which intensifies the stress concentration of the metatarsal. The point of force on the face shifts forward to the outside, and the gravity line gradually shifts to the lower tibiofibular joint.
Discuss
The pathology of the foot and ankle joints of children with flatfoot is a pathological process that gradually develops due to changes in the shape and force of bones, muscles, and ligaments, and eventually progresses to irreversible joint deformities, which seriously affect the children’s study and life.
In the treatment of flat feet, the effectiveness of early prevention is far greater than that of remedial treatment. Therefore, the inducements of flatfoot-obesity, malnutrition, too little exercise, etc., should be removed, so that the foot bones have a good development environment under appropriate weight-bearing.
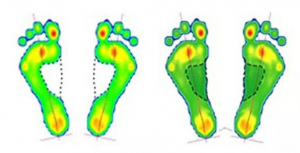
Instruct children to strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the foot and ankle joint to maintain the shape of the arch, such as instructing children to exercise the strength of interosseous muscles, lumbricoid muscles, and plantar longus muscles through the feet Clamping the ball improves the passive traction of the plantar longus and vermiform muscles, exercises the strength of the tibial anterior muscle by alternately walking on the toe and walking on the heel, and relaxes the muscles in time after the exercise, improves the blood circulation of the ankle, and strengthens the sole Muscle strength, maintain and improve arch elasticity. Reduce the frequency of wearing tourist shoes, avoid standing for a long time, and correct the lifestyle habits such as walking outside
